Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) occurs when relaxed throat muscles repeatedly block airflow during sleep, leading to drops in blood oxygen and frequent sleep disruptions. Untreated OSA can cause excessive daytime fatigue and significantly increase the risk of serious health conditions, including high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, diabetes, depression, and accidents. Risk factors include obesity, male gender, aging, large neck circumference, smoking, alcohol or sedative use, nasal obstruction, and certain anatomical features of the airway. Early evaluation and treatment are essential to reduce long-term complications.
Sleep Apnea: Causes, Complications & Risk Factors
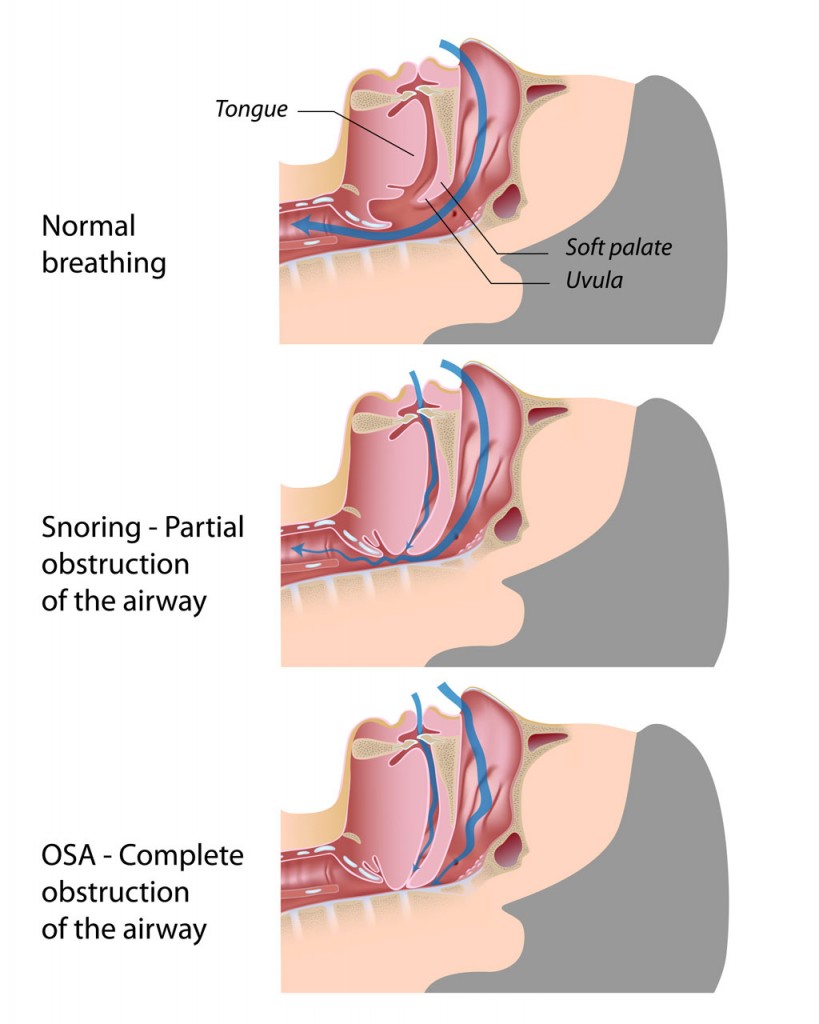 Obstructive sleep apnea typically occurs due to throat muscles relaxing causing the patient’s airway to narrow or close, whereby an adequate amount of air cannot be taken in. This lack of air can cause the oxygen level in the blood to lower. Patients may gasp, snort, or choke to the point of awakening in order to reopen the airway.
Obstructive sleep apnea typically occurs due to throat muscles relaxing causing the patient’s airway to narrow or close, whereby an adequate amount of air cannot be taken in. This lack of air can cause the oxygen level in the blood to lower. Patients may gasp, snort, or choke to the point of awakening in order to reopen the airway.
The sleep disruptions are often so brief that the patient is unaware of awakening; however, because the pattern can occur anywhere from 5 to over 30 times per hour, all night, patients never achieve the desired sleep necessary to feel rested.
Complications of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) makes healthy, restorative sleep impossible, therefore daytime fatigue is the most common complication of OSA. Because sleep apnea causes sudden drops in oxygen levels, OSA sufferers are at risk for many other serious health conditions:
- High blood pressure (hypertension): Low blood oxygen levels increases blood pressure.
- Heart attack
- Atrial fibrillation: An irregular beating of the heart.
- Heart failure
- Stroke
- Diabetes: OSA patients have a greater likelihood of developing insulin resistance.
- Liver problems: OSA patients are more prone to liver scarring and are more apt to have abnormal liver function test results.
OSA can cause complications with certain medications or general anesthesia, and is generally a concern when sedation or surgery is required. Patients with underlying heart disease are also at greater risk from sleep apnea because the irregular heartbeat caused by oxygenation drops can lead to sudden death. Other risks of OSA are:
- Increased stress levels: The release of stress hormones can be triggered by OSA.
- Memory loss
- Skin aging
- Relationship difficulties: Often due to a sleep partner being kept awake or moving locations due to snoring.
- Increased risk of workplace and motor vehicle accidents: Due to sleepiness or difficulty in concentrating.
- Depression: Patients with OSA are 3 times more likely to suffer from depression.
Risk Factors for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can occur at any age and affect anyone, but is 2 times more likely to affect males than females. The risk of having OSA significantly increases with age, and does develop more frequently when certain risk factors are present:
- Obesity: People who carry excess weight are 4 times more likely to have sleep apnea than those considered to be of normal weight. Obesity changes pharyngeal shape and size which can block the upper airway. Fat deposits in the neck can also obstruct breathing.
- Large neck circumference: Men with a neck circumference over 17 inches and women with neck circumference over 16 inches are at higher risk.
- Family history
- Alcohol or sedative use: Use of these substances, especially near bedtime, can relax throat muscles and cause or worsen sleep disordered breathing.
- Smoking: Smoking can increase inflammation and fluid retention in the throat. People who smoke are 3 times more likely to experience OSA than those who don’t smoke.
- Nasal congestion: Recurrent allergies can contribute to mouth breathing and increase the likelihood of OSA.
Clinical risk factors for sleep disordered breathing include:
- Cranial abnormalities
- Nasal obstruction
- Overbite (mandibular retrognathia)
- Undersized jaw (micrognathia)
- Narrow, short or tapered maxillary arch
- Soft, long palate
- Modified Mallampati Class III or IV
- Enlarged tongue (macroglossia) or tonsils (tonsillar hypertrophy)
If you have any issues with snoring or possibly obstructive sleep apnea and would like an appointment with one of our physicians at Fort Worth ENT & Sinus, please complete an online appointment request or phone 817-332-8848.
Frequently Asked Questions
During obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), the throat muscles relax and partially or completely block the airway while sleeping. This causes brief pauses in breathing, drops in blood oxygen, and frequent sleep interruptions. Over time, these disruptions prevent restorative sleep and can stress the heart, brain, and other organs.
Untreated OSA can lead to serious complications, including high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, diabetes, liver problems, and increased risk of accidents. It can also contribute to daytime fatigue, memory issues, mood disorders, and difficulties in relationships due to disrupted sleep.
OSA can affect anyone, but the risk is higher in men, people over 40, and those who are overweight. Other risk factors include a large neck circumference, family history, nasal obstruction, smoking, alcohol or sedative use, and certain anatomical features such as a small jaw, enlarged tonsils, or a long soft palate.
Yes. Sleep apnea can increase stress hormone levels, contribute to memory problems, and raise the risk of depression. Patients with OSA are about three times more likely to experience depression compared to people without the condition, largely due to poor sleep quality and oxygen deprivation.
Diagnosis typically involves a sleep study (polysomnography) to monitor breathing, oxygen levels, and sleep patterns. Treatment may include lifestyle changes (weight loss, avoiding alcohol or sedatives), CPAP or other airway devices, oral appliances, and in some cases, surgery to correct airway blockages. Early evaluation is important to prevent long-term health complications.


