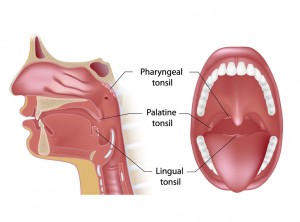
Tonsil and adenoid surgery may be necessary due to chronic or recurring infections, sore throat, halitosis, or tonsil enlargement causing difficulty breathing during sleep. The latter can lead to snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Surgery can be very effective in treating these problems. The tonsils are small glands visible on each side of the back of the throat. Adenoids consist of the same tissue, but hidden behind the soft palate. They serve as a meeting place for our immune system to communicate. However, having your tonsils and adenoids removed will not affect your body’s immunity.
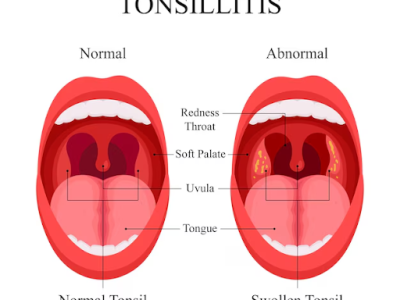
What is Tonsillitis?
Acute tonsillitis is usually caused by an infection. Typical symptoms include sore throat, possible fever, trouble swallowing and enlarged, swollen glands in the neck. The throat is typically swollen/red and there may even be small yellow or white spots on the tonsils. Initial treatment is generally antibiotics, but multiple infections may suggest to your physician that removal is necessary. Usually, the recommendation is to remove them if acute tonsillitis occurs more than 7 times in a year, 5 times in two consecutive years, or 3 times in 3 consecutive years. There are several other indications for tonsillectomy that may be discussed with your ENT.
 The most common reason for tonsillectomy today is upper airway resistance syndrome, or obstructive sleep apnea. In these conditions, enlarged tonsils (and adenoids) obstruct breathing during sleep. Symptoms include loud snoring, gasping for air, pauses in breathing during sleep, and daytime sleepiness. If you or your child has these symptoms, t&a surgery (tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy) may be needed.
The most common reason for tonsillectomy today is upper airway resistance syndrome, or obstructive sleep apnea. In these conditions, enlarged tonsils (and adenoids) obstruct breathing during sleep. Symptoms include loud snoring, gasping for air, pauses in breathing during sleep, and daytime sleepiness. If you or your child has these symptoms, t&a surgery (tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy) may be needed.
Technique for Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy
The current method we utilize for T&A surgery is Coblation®. This technique uses radiofrequency energy to dissect through natural tissue planes and remove/shrink tissue. The energy generated by the device is cooler than traditional techniques, and as a result, is less traumatic to the surrounding tissue. This is felt to decrease pain after the procedure and reduce recovery time compared with other techniques. The surgery takes approximately 30 minutes and is performed as an outpatient procedure in most cases. Patients should expect a sore throat for at least 7-10 days after surgery. 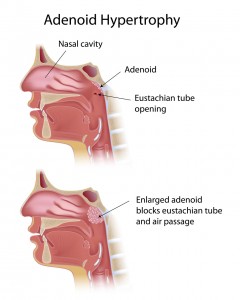
Preparation For Tonsillectomy
For procedures in the hospital or surgical center, nothing to eat after midnight (no solid food or liquids) the day before the procedure. An empty stomach is mandatory before surgery, both from a safety point of view and a practical point of view as, it helps reduce perioperative nausea and vomiting. All blood thinners, aspirin-containing medications and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication (“Advil”, “Motrin”, etc.) should be discontinued at least 10 days before surgery, as these drugs can prevent blood from clotting and increase the risk of postoperative bleeding. Certain other medications may need to be discontinued before surgery. If you are not sure, please ask our physicians.
Postoperative Care Following a Tonsillectomy
Somebody should be prepared to drive you home after tonsils and adenoids surgery. The pain medication administered during surgery and postoperatively is not safe for use during driving (or operating any machinery).
For postoperative pain control following tonsils and adenoids surgery, your physician will usually prescribe a narcotic-containing medication. It is imperative that you take the medication exactly as prescribed. If the pain is intolerable, or if you have any significant post-operative bleeding (more than a tablespoon), you should contact your doctor immediately.
Postoperative diet generally consists of softer foods and liquids. Drinking plenty of fluids is encouraged, but patients should avoid carbonated beverages, spicy foods, citrus fruits and any food that may scrape the throat (as this may increase the risk of bleeding). No heavy lifting, exercise, sports or travel is permitted for 2-3 weeks after surgery. Most adults should be able to return to work after about a week.
Please call our office at 817-332-8848 to set up an appointment or submit an online appointment request.