Tympanoplasty and mastoidectomy, together known as a tympanomastoidectomy, are two surgical procedures often performed at the same time on a patient’s ear to control chronic infection and restore hearing. 
Tympanoplasty and Mastoidectomy Surgery
Mastoidectomy
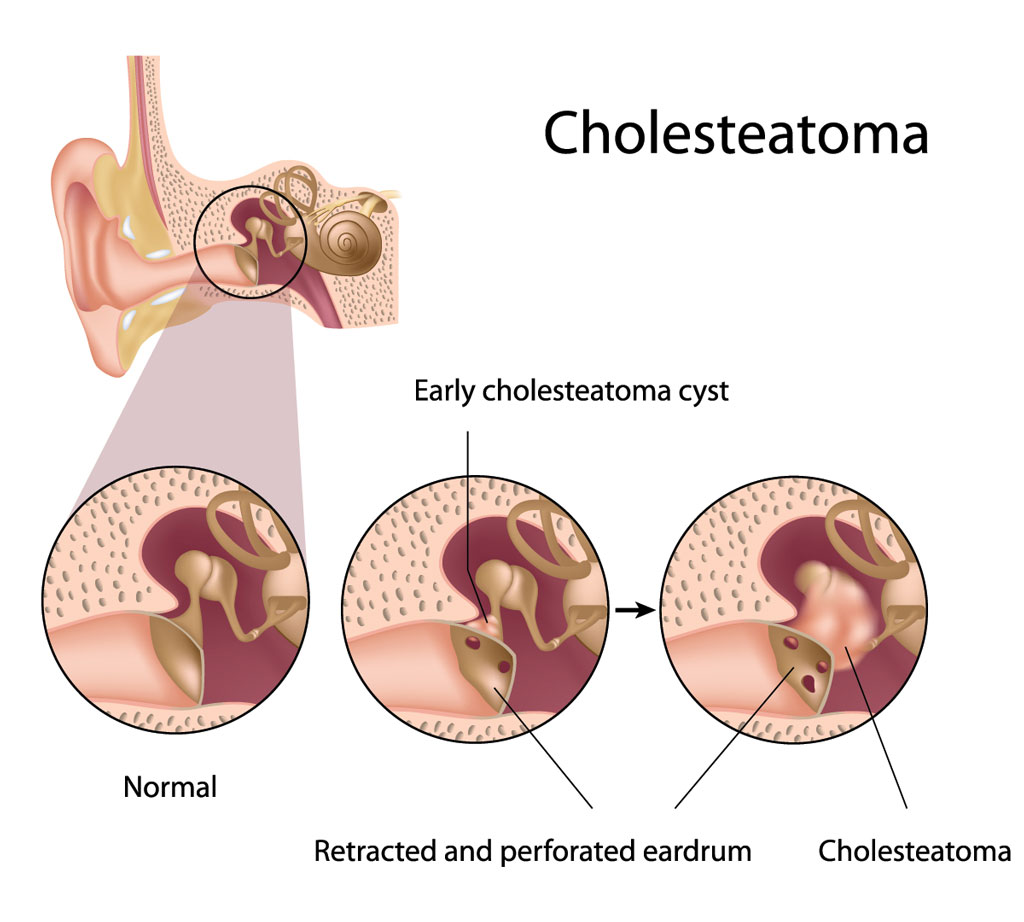
Mastoidectomy is the portion of the operation in which the surgeon removes diseased air cells (cholesteatoma matrix) from the mastoid bone. These diseased cells lie behind the honeycombed cavity (mastoid) in the temporal bone located at the sides and base of the skull behind the ear.
Mastoidectomy is typically required for patients with middle ear infections (chronic otitis media – COM), a long-standing infection affecting the middle ear and frequently accompanied by cholesteatoma (a destructive, non-cancerous skin cyst) or an unhealed eardrum perforation. This infection, if left untreated, can spread into the skull, as well as cause significant hearing loss, dizziness, and brain erosion.
Tympanoplasty
T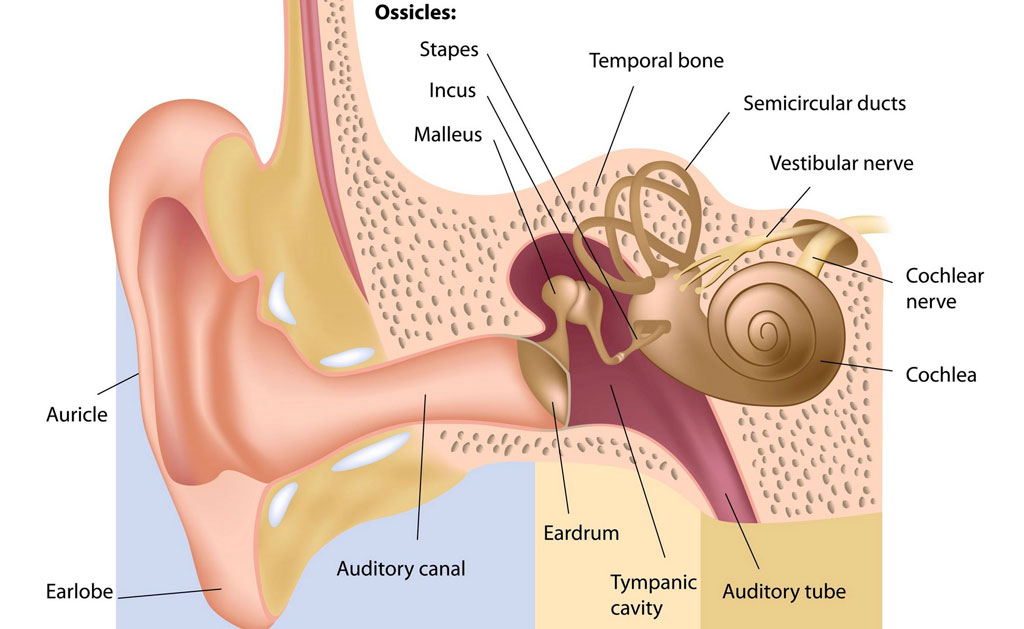 ympanoplasty is the surgical procedure which restores and/or retains hearing. During the tympanoplasty, the surgeon will graft the tympanic membrane (eardrum) and reconstruct the middle ear. A prosthetic device may need to be implanted to replace the ossicles (middle ear bones) that have been damaged by infection.
ympanoplasty is the surgical procedure which restores and/or retains hearing. During the tympanoplasty, the surgeon will graft the tympanic membrane (eardrum) and reconstruct the middle ear. A prosthetic device may need to be implanted to replace the ossicles (middle ear bones) that have been damaged by infection.
Types of prosthetics used to replace the ossicles may be:
- T.O.R.P. (Total Ossicular Replacement Prosthesis)
- P.O.R.P. (Partial Ossicular Replacement Prosthesis)
The goal of tympanoplasty is to close any perforation, as well as improve hearing.
The Tympanomastoidectomy Procedure
Tympanomastoidectomy procedure is performed in a hospital setting under general anesthesia and typically takes several hours. During the tympanomastoidectomy, incisions are made inside and behind the infected ear. The middle ear and mastoid bone are opened and the infected tissue or the cholesteatoma is removed. The eardrum is repaired with muscle lining from behind the ear.
After the tympanomastoidectomy is completed, the surgeon will place packing inside the ear to keep tissues in place as they heal. Most tympanomastoidectomy patients can be released after an overnight observation, unless they are experiencing nausea or dizziness.
 Tympanoplasty and Mastoidectomy Postoperative Instructions
Tympanoplasty and Mastoidectomy Postoperative Instructions
Tympanoplasty and Mastoidectomy recovery typically involves 1-2 weeks off of work or school. An initial follow-up appointment should take place one week after surgery for suture removal, after which most normal activity can resume. Packing will be removed periodically as the ear heals.
In some cases, a minor skin grafting procedure (Thiersch grafting) may need to be performed to assist the healing process and avoid infection. During Thiersch grafting, a layer of skin from the inside of the upper arm is transplanted over the surgical area in the ear. This grafting is usually done 10 days after the patient undergoes the tympanomastoidectomy.
It is important to closely follow your doctor’s instructions after the tympanomastoidectomy, including:
- Do not blow your nose for at least 2 weeks after your procedure. Blowing the nose can cause pressure build-up in the ear and displace the eardrum patch. If you sneeze, keep your mouth open.
- Do not allow any water to enter the ear. Place Vaseline-coated cotton inside the ear while showering. Any water in the ear can cause infection.
- Do not fly for 6 weeks after surgery. Air pressure changes could negatively impact your recovery.
- Apply antibiotic ointment to the ear canal and the incision behind the ear, as instructed.
- Avoid heavy lifting or being fatigued.
- Take antibiotic and pain medications as directed.
It is normal, after a tympanomastoidectomy, to have a bloody or watery discharge from the ear canal, as well as from behind the ear. You may experience some popping sounds in the ear during the first few months after surgery, as the ear heals. You should not be concerned about your hearing for 6-8 weeks after the tympanomastoidectomy, at which time your hearing will be evaluated.
You should contact your doctor if you develop:
- Fever over 101˚
- Foul smelling ear drainage
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
- Worsening redness or swelling around the incision
- Leg swelling or pain
- Persistent drainage from behind the ear after 10 days
Possible Complication of Tympanomastoidectomy
As with any surgery, there can be complications and risks associated with having a tympanomastoidectomy. Some possible complications include:
- Dizziness: It is common to experience some unsteadiness for a few days after a tympanomastoidectomy. Sudden head movements may cause dizziness for a few weeks. On rare occasions, prolonged dizziness may occur.
- Dry mouth and change in taste (often metallic or sour taste): These side effects may occur for a few weeks after surgery and, in approximately 5% of patients, may last longer.
- Tinnitus: Ringing, hissing, or popping noise in the ear may occur or be more noticeable.
- Hearing loss: Hearing can worsen after a tympanomastoidectomy if the bones cannot be reconstructed during surgery, but can usually be corrected with a follow-up procedure. Severe hearing loss can occur in approximately 1% of patients.
- General anesthesia problems: A small percentage of patients may experience complications with general anesthesia, including cardiac arrhythmia or breathing problems.
Rare complications can include:
- Facial weakness: Any paralysis is usually temporary on one side of the face due to swelling or abnormality of a facial nerve. Permanent paralysis is extremely rare.
- Eye problems: Treatment by a specialist could be necessary.
- Infection: On the rare occasion that an infection occurs, it could lead to meningitis, which may require lengthy antibiotic treatment, as well as hospitalization. Infection can also be associated with the eardrum failing to heal (approximately 5% of cases).
- Hematoma: Blood may collect under the skin incision which may require surgical removal or prolonged hospitalization.
If you experience any complications following tympanoplasty and mastoidectomy, you should contact our office as soon as possible.
Please call our office at 817-332-8848 to set up an appointment or submit an online appointment request.


